The retreat of glaciers due to climate change is reshaping mountain landscapes and biodiversity. While previous research has documented vegetation succession after glacier retreat, our understanding of functional diversity dynamics is still limited. In this case study, we address the effects of glacier retreat on plant functional diversity by integrating plant traits with ecological indicator values across a 140-year chronosequence in a subalpine glacier landscape. We reveal that functional richness and functional dispersion decrease with glacier retreat, while functional evenness and functional divergence increase, suggesting a shift toward more specialized and competitive communities. Our findings highlight the critical role of ecological factors related to soil moisture, soil nutrients and light availability in shaping plant community dynamics. As years since deglaciation was a key factor in regression and machine learning models, encapsulating time-lagged, spatial and historical processes, we highlight the need of including time into phenomenological or mechanistic models predicting biodiversity change following glacier retreat. The integrative approach of this case study provides novel insights into the potential response of alpine plant communities to climate change, offering a deeper understanding of how to predict and anticipate the effects of glacier extinction on biodiversity in rapidly changing environments. (sic)(sic): (sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)140(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).
Arctic ecosystems are highly vulnerable to ongoing and projected climate change. Rapid warming and growing anthropogenic pressure are driving a profound transformation of these regions, increasingly positioning the Arctic as a persistent, globally significant source of greenhouse gases. In the Russian Arctic-a critical zone for national economic growth and transport infrastructure-intensive development is replacing natural ecosystems with anthropogenically modified ones. In this context, Nature-based Solutions (NbS) represent a vital tool for climate change adaptation and mitigation. However, many NbS successfully applied globally have limited applicability in the Arctic due to its inaccessibility, short growing season, low temperatures, and permafrost. This review demonstrates the potential for adapting existing NbS and developing new ones tailored to the Arctic's environmental and socioeconomic conditions. We analyze five key NbS pathways: forest management, sustainable grazing, rewilding, wetland conservation, and ecosystem restoration. Our findings indicate that protective and restorative measures are the most promising; these can deliver measurable benefits for both climate, biodiversity and traditional land-use. Combining NbS with biodiversity offset mechanisms appears optimal for preserving ecosystems while enhancing carbon sequestration in biomass and soil organic matter and reducing soil emissions. The study identifies critical knowledge gaps and proposes priority research areas to advance Arctic-specific NbS, emphasizing the need for multidisciplinary carbon cycle studies, integrated field and remote sensing data, and predictive modeling under various land-use scenarios.
Bare land exposed by glacier retreat provides new opportunities for ecosystem development. Investigating primary vegetation succession in deglaciated regions can provide significant insights for ecological restoration, particularly for future climate change scenarios. Nonetheless, research on this topic in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has been exceedingly limited. This study aimed to investigate vegetation succession in the deglaciated area of the Zepu glacier during the Little Ice Age in southeastern Tibet. Quadrat surveys were performed on arboreal communities, and trends in vegetation change were assessed utilizing multi-year (1986-2024) remote sensing data. The findings indicate that vegetation succession in the Zepu glacier deglaciated area typically adheres to a sequence of bare land-shrub-tree, divided into four stages: (1) shrub (species include Larix griffithii Mast., Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis Rousi, Betula utilis D. Don, and Populus pseudoglauca C. Wang & P. Y. Fu); (2) broadleaf forest primarily dominated by Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis Rousi; (3) mixed coniferous-broadleaf forest with Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis Rousi and Populus pseudoglauca C. Wang & P. Y. Fu as the dominant species; and (4) mixed coniferous-broadleaf forest dominated by Picea likiangensis (Franch.) E. Pritz. Soil depth and NDVI both increase with succession. Species diversity is significantly higher in the third stage compared to other successional stages. In addition, soil moisture content is significantly greater in the broadleaf-dominated communities than in the conifer-dominated communities. An analysis of NDVI from 1986 to 2024 reveals an overall positive trend in vegetation recovery in the area, with 93% of the area showing significant vegetation increase. Temperature is the primary controlling factor for this recovery, showing a positive correlation with vegetation cover. The results indicate that Key ecological indicators-including species composition, diversity, NDVI, soil depth, and soil moisture content-exhibit stage-specific patterns, reflecting distinct phases of primary succession. These findings enhance our comprehension of vegetation succession in deglaciated areas and their influencing factors in deglaciated areas, providing theoretical support for vegetation restoration in climate change.
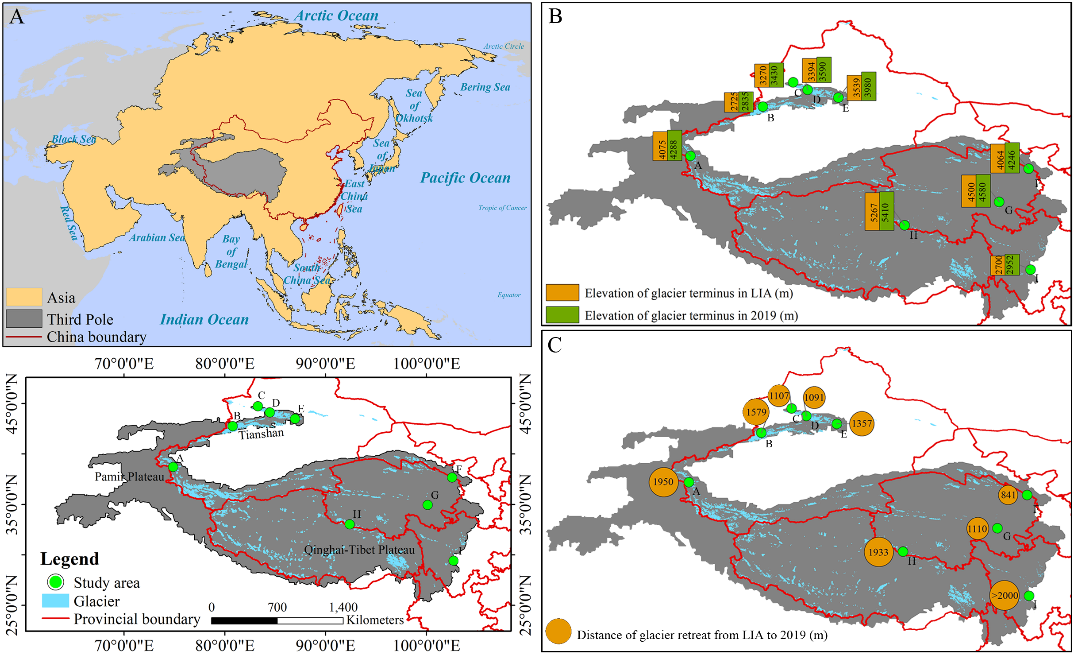
青藏高原及周边高山地区统称为“第三极”地区,是除南北极外最大的冰川集中区。在全球气候变暖背景下,第三极地区正经历显著增温,气温上升加速了冰川消融,进而影响区域生态平衡。第三极冰川前缘作为海拔最高的陆地脆弱生境之一,对气候及冰川变化响应敏感。深入了解冰川前缘植被动态,对科学评估冰缘生态系统响应气候至关重要。然而,受制于观测条件,目前仍缺乏对该地区冰缘植被的大范围系统性观测研究。 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院上官冬辉研究员团队与兰州交通大学、中巴地球科学联合研究中心及南通大学相关研究团队合作,选取第三极地区9条代表性冰川,在其前缘布设样地并获取植被信息。利用植被指数量化了冰川退缩时间序列上植物群落特征的变化,并结合植物区系相似性指数,系统分析了不同样地间及不同冰川前缘间的植物区系相似性。 研究显示,物种多样性和植被盖度沿冰川退缩时间序列呈波动增加趋势,且在海洋性冰川前缘的增加速率尤为显著。所有冰川前缘的植物生活型在演替早期阶段较为相似,但随着演替推进,生活型组成开始分化,在不同类型冰川前缘间差异更为明显。此外,不同冰川前缘间具有植物区系相似性,其中地理位置邻近且属于同一类型冰川的前缘地区植物区系相似性最高。 该研究揭示了局地气候与地理因子在塑造冰川前缘生态系统及植物区系格局中扮演的关键作用,为阐明气候变化对冰川前缘生态系统的影响提供了科学依据,并为区域生物多样性保护工作提供了理论指导。 该成果以Vegetation successional dynamics and floristic similarity across various glacier forelands in the third pole为题发表于国际知名学术期刊Global and Planetary Change上。兰州交通大学魏天锋副教授为本文第一作者,西北研究院上官冬辉研究员为本文通讯作者。研究得到中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(A类)和国家自然科学基金等项目的资助。 论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2025.104916 (A)研究区地理区位图,(B)被研究冰川在小冰期和2019年的冰川末端海拔,(C)被研究冰川在小冰期至2019年间的冰川退缩距离
2025-06-09 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院Glacier forelands provide ideal natural laboratories for studying primary vegetation succession. However, understanding of vegetation dynamics on glacier forelands in the Third Pole (TP) region remains limited. In this study, we employed field sampling and aerial photography to investigate key vegetation parameters (species composition, species diversity, and fractional vegetation cover (FVC)) along chronosequences on nine representative glacier forelands of the TP, spanning continental, subcontinental, and maritime glacier types, then analyzed vegetation changes along successional gradients and assessed floristic similarity both within and among the glacier forelands. Our results showed that species diversity and FVC generally exhibited increasing trends, with fluctuations from young to old forelands. These parameters increased more rapidly on maritime glacier forelands. Plant life-forms were similar during the early stages across all forelands but began to diverge as succession progressed, particularly between different glacier types. Furthermore, floristic similarity was observed between glacier forelands, with the highest similarity occurring between forelands of the same glacier type in adjacent geographic locations. Our findings highlight the critical roles of local climate and geographic factors in shaping proglacial ecosystems and flora, providing a scientific basis for understanding the effects of climate change on proglacial ecosystems and guiding biodiversity conservation efforts.
This study explored the effects of forest fires on soil microbial activity in forest soils classified by rock origin (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) and stratified by subsoil depth (topsoil, subsoil). Microbial activity, indicated by average well color development (AWCD) and Shannon diversity indices, was higher in undamaged topsoils compared to fire-damaged ones. In contrast, fire-damaged subsoils, particularly in metamorphic and sedimentary soils, exhibited increased microbial activity over time due to organic matter decomposition. A significant increase in substrate utilization was observed in undamaged soils across all rock types (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01) in topsoil, with sedimentary rock exhibiting the highest microbial diversity based on Shannon indices. The dehydrogenase activity followed a similar pattern, with reduced activity in fire-damaged topsoil but higher activity in damaged metamorphic and sedimentary subsoils. Principal component analysis (PCA) linked microbial indicators (AWCD, Shannon index) to mineral compositions like orthoclase and hornblende, highlighting the role of soil chemistry in shaping microbial responses to fire. These insights advance the understanding of fire-induced changes in soil microbial functions across diverse geological contexts.
Black truffle, Tuber melanosporum Vittad., production is increasing due to an improvement in cultivation management and to the demand for this highly appreciated fungus. However, this intensification of truffle cultivation has led to the appearance of problems related to pest incidence. Specifically, the truffle beetle, Leiodes cinnamomeus (Panzer, 1793) (Coleoptera: Leiodidae), causes significant losses in black truffle marketability. However, its biology is still poorly known, and no effective agro-ecological methods exist to mitigate its damage to the truffles. This study aimed at assessing the population dynamics of L. cinnamomeus over four seasons (2019-2023) in an orchard located in NE Spain and relating these dynamics to weather variables and damage to truffle fruit bodies. Moreover, we described the diversity of arthropods captured in the traps in search of potential natural enemies of this beetle. The maximum population peak was observed in November, except for a single season in which it occurred in December. Moreover, the sex ratio was balanced (0.54 on average), but it varied over the growing season and among years. Significant and positive relationships of the population density of truffle beetles with air temperature and relative humidity were observed. The number of beetles per trap and day was strongly linked to heat accumulation. Finally, the Carabid Percus (Pseudopercus) patruelis (L. Daufour, 1820) was identified as a natural enemy of L. cinnamomeus. These results could be used in the future for monitoring and predicting truffle beetle populations.
Intensive agriculture development and achievement to higher profitability has inflicted permanent damage on agroecosystems. Rapid deterioration of structure and functional properties in agroecosystems has intensified the need for research on agroecosystem health and management. To assess the health status of wheat agroecosystems in the agricultural lands of Bandar-e-Turkmen county (Golestan province, Iran), we were used the variables of weed and natural enemies biodiversity, soil health (carbon and organic matter, microbial respiration, earthworm, soil salinity, and acidity), environmental indexes (environmental effects of pesticides (EIQ) and nitrate leaching) and vegetation indexes (RVI, cultivar type, and grain yield). In this study, thematic layers were prepared in ArcGIS and overlayed according to three scenarios. Then final layer was classified into three classes of health. Based on the results, only 8.47% (5 fields) were located in the first health class. These fields were characterized by high grain yield, low weed biodiversity, minimal pesticides use, optimal soil conditions, high RVI, and the presence of earthworms and natural enemies. Also, we found that 42 fields (71.19%) were placed in the second health class. Increase of biodiversity and population of weeds, lower grain yield, and reducing the quantity and quality of soil variables were important factors that reduced the health degree of these fields. Based on the results, 20.34% of the area (12 fields) in the central and western parts of the county was placed in the unhealthy class. It seems that increasing the environmental restrictions, including salinity higher than 6 ds/m, high weed diversity, increasing the consumption of harmful and dangerous pesticides with high environmental impact, and less grain yield than the potential of cultivars, were the main reasons for placing these fields in the unhealthy class. Also, the most important factors of decreasing the health degree of fields, frequency of weeds, increasing consumption of chemical pesticides, low soil organic matter, absence of earthworms, and decreasing grain yield were identified. Generally, management of weeds, implementation of crop rotation, preservation of plant residues on the soil surface, and development of conservation agriculture can help to improve the health indicators of wheat agroecosystems.
Understanding the spatiotemporal dynamics of microbial communities is essential for predicting their ecological roles and interactions with host plants. In a recent study, Wei and colleagues (Microbiol Spectr 13:e02097-24, 2024) investigated fungal diversity across multiple plant and soil compartments in rubber trees over two seasons and two geographically distinct regions in China. Their findings revealed that alpha diversity was primarily influenced by seasonal changes and physicochemical factors, while beta diversity exhibited a strong geographical pattern, shaped by leaf phosphorus and soil available potassium. These results highlight the role of environmental drivers in shaping within-community diversity, while other factors contribute to the differences between fungal communities across the soil-plant continuum. By distinguishing the effects of temporal and spatial factors, this study provides detailed insights into plant-associated microbiomes and emphasizes the need for further research on the functional implications of microbial diversity in the context of changing environmental and agricultural conditions.
AimsPecan (Carya cathayensis Sarg.) is an important forest trees in China, the application of chemical pesticides for disease control has caused severe damage to the soil, including reduced fertility and disruption of microbial communities. Although Trichoderma treatment has been shown to promote plant growth and improve soil quality, its effects on the growth promotion of pecan and the impact on soil microbial communities and physicochemical properties remained unclear.MethodsIn this study, we investigated the impact of T. asperellum TCS007 spore suspension and its fermented crude extract on the growth and development of pecan seedlings. We also explored the effects of TCS007 treatment on the nutrients, enzyme activities, and microbial diversity in the rhizosphere soil of pecan seedlings during their three main growth stages.ResultsTreatment with TCS007 spore suspension or crude extract promoted the growth of pecan seedlings, with significantly higher levels of leaf hormones and defense enzyme activity compared to the control (CK). Moreover, the content of soil organic matter and ammonium nitrogen, as well as the activity of soil enzymes such as catalase and urease, were all significantly higher than CK after treatment, and the soil pH shifted from slightly acidic to slightly alkaline. The results indicated that TCS007 treatment significantly increased the richness of beneficial fungi and bacteria in the soil.ConclusionThe results demonstrated that TCS007 treatment significantly promoted the growth of pecan plants, increased enzyme activity and nutrient content in the soil, and improved the soil micro-ecological environment.