Global warming is accelerating the glacier and snow shrinkage in the Tien Shan. This study assesses the impacts of meltwater changes on soil moisture and hydrological processes using VIC-CAS, a glacier-expanded Variable Infiltration Capacity model, refined by improving the glacier-melt algorithm and incorporating a snowmelt pathway-tracking scheme. Projections were conducted across six glacierized basins in the Northern Tien Shan, with model calibration and validation using remote-sensing snow/glacier data and observed streamflow. By the late century (2080-2100), snowmelt runoff will decrease by one-third to two-thirds owing to decreasing snowfall. In the Bayingou River Basin (BRB), comprising large glaciers, glacier retreat is slow, and glacier runoff will increase until the 2060s. In contrast, glacier runoff in the other five basins, having surpassed the glacier runoff tipping points, will decline substantially. Glacier runoff remains the primary driver of annual streamflow variability with the BRB showing little change, while the other basins experience a one-fourth decrease in annual streamflow by the late 21st century. Reduced summer meltwater will exacerbate water scarcity, with summer streamflow declining by over one-third in basins with declining glacier runoff, and by nearly 10 % in the BRB. In mountainous areas above 2000 m, increased evapotranspiration is projected to reduce annual mean soil moisture by 10.5-16.3 % by the late century, with a more substantial decrease of 12.4-20 % during July-September due to reduced snowmelt. Continued glacier and snow shrinkage will intensify hydrological and ecological droughts, posing major challenges for water resource management and ecological protection.
BackgroundAccelerated glacial retreat driven by climate change is rapidly reshaping alpine and polar environments, exposing deglaciated terrains that serve as critical sites for microbial colonization and early ecosystem development. These newly exposed substrates provide a unique setting for studying primary microbial succession, the onset of soil formation, and the initiation of biogeochemical cycles, particularly carbon cycling. Microbial communities, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, and viruses, play pivotal roles in regulating elemental fluxes and establishing foundational ecosystem processes in these nascent landscapes.ResultsRecent studies highlight substantial shifts in microbial community structure and function across different glacial forefields and cryospheric habitats. Microbial assemblages display pronounced spatial heterogeneity shaped by physicochemical gradients and successional age. Functional analyses reveal diverse metabolic pathways involved in carbon fixation, organic matter transformation, and long-term carbon storage. Additionally, viral populations emerge as influential regulators of microbial metabolism and potential archives of past environmental conditions. The assembly of these communities is influenced by a combination of abiotic factors, dispersal mechanisms, and local adaptation, with cascading effects on carbon fluxes and nutrient dynamics.ConclusionsMicrobial processes in deglaciated environments are central to early biogeochemical transformations and represent key drivers of carbon sequestration in retreating glacial landscapes. Understanding the ecological roles, functional diversity, and climate sensitivity of these microbial communities is essential for projecting biogeochemical and climate system feedbacks in the context of ongoing glacial loss. Integrating microbial ecology into Earth system models will enhance predictions of carbon dynamics and inform conservation and climate mitigation strategies in polar and alpine regions.
The retreat of glaciers due to climate change is reshaping mountain landscapes and biodiversity. While previous research has documented vegetation succession after glacier retreat, our understanding of functional diversity dynamics is still limited. In this case study, we address the effects of glacier retreat on plant functional diversity by integrating plant traits with ecological indicator values across a 140-year chronosequence in a subalpine glacier landscape. We reveal that functional richness and functional dispersion decrease with glacier retreat, while functional evenness and functional divergence increase, suggesting a shift toward more specialized and competitive communities. Our findings highlight the critical role of ecological factors related to soil moisture, soil nutrients and light availability in shaping plant community dynamics. As years since deglaciation was a key factor in regression and machine learning models, encapsulating time-lagged, spatial and historical processes, we highlight the need of including time into phenomenological or mechanistic models predicting biodiversity change following glacier retreat. The integrative approach of this case study provides novel insights into the potential response of alpine plant communities to climate change, offering a deeper understanding of how to predict and anticipate the effects of glacier extinction on biodiversity in rapidly changing environments. (sic)(sic): (sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)140(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic),(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic)(sic).
The Third Pole region, encompassing the vast Himalayan and Tibetan Plateau, is undergoing rapid cryosphere and ecological transformations. This review synthesizes findings from 93 peer-reviewed studies (2000-2024) to evaluate the interactions between glacier retreat, permafrost degradation, and material cycling (carbon, methane, and nitrogen). Mean air temperature has increased by 0.3-0.4 degrees C per decade, while glaciers have lost nearly 36% of their area since the 1990s. Permafrost active layer thickness has deepened by more than 50%, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4) previously locked in frozen soils into the atmosphere and water systems. Methane fluxes from wetlands, lakes, and hydrates amplify warming feedback, while nitrogen deposition and fertilizer inputs alter ecosystem nutrient cycling and elevate nitrous oxide (N2O) risk. These processes intensify feedback loops that accelerate regional and global climate change. The findings highlight the Third Pole's role as both a critical water tower for Asia and a major contributor to global greenhouse gas budgets under warming scenarios. Effective policy responses require black carbon mitigation, GLOF early warning systems, permafrost-resilient infrastructure, sustainable nitrogen management, and regional data-sharing platforms. Future research should prioritize long-term monitoring, interdisciplinary flux measurements, and integrative modeling to better capture cryosphere-hydrosphere-biosphere-atmosphere interactions. The stability of the Third Pole is a must for global climate resilience.
The terrestrial program of the Arctic Challenge for Sustainability-II (ArCS II) is dedicated to clarifying the complex responses of Arctic boreal ecosystems and biogeochemical cycles to a warming climate. Focusing on ecosystem function, terrestrial greenhouse gas dynamics, and permafrost and biogeochemical cycles, ArCS II targets key challenges posed by climate change across terrestrial ecosystems. Biodiversity and ecosystem function research emphasizes the interactions between plant and soil microbial communities across Arctic boreal regions, with discoveries such as new fungal species contributing valuable information elucidating the status of Arctic ecosystems. Our study revealed that vegetation has a significant impact on the composition and network structure of microbial communities, and these interactions may influence ecosystem responses to environmental changes. Greenhouse gas dynamics were analyzed using long-term carbon and methane emissions data collected in boreal forests, tundra, wetlands, and glacial termini, as emissions from these regions can accelerate warming. Plant-mediated methane transport was identified as the primary process driving methane emission from wetlands, and elevated methane concentrations were detected in some glacial meltwaters. ArCS II advances permafrost modeling to assess the impacts of thawing on terrestrial processes, emphasizing freeze-thaw cycles and their impact on greenhouse gas dynamics. Excess ice formed within permafrost plays a role in suppressing permafrost warming and may induce anomalous variations in greenhouse gas emissions. Despite limitations imposed on field surveys by COVID-19, the ArCS II project elucidated ecosystem changes using long-term data. ArCS II terrestrial research lays a foundation for the exploration of climate impacts on Arctic boreal ecosystems.
This study examines permafrost thermal regimes and hydrological responses to climate change in the Navarro Valley, Chile's Dry Central Andes, using a decade of ground temperature data (2013-2022) from two rock glaciers-RG1 (3805 m) and RG2 (4047 m)-alongside short-term meltwater conductivity records, meteorological data, and long-term streamflow records. We assess permafrost stability and climatic sensitivity by analyzing thermal offset data (2017-2022) and ground temperature trends. Both sites show sustained warming, but RG1 exhibits accelerated warming (+ 2.84 degrees C/decade), frequent freeze-thaw cycles, and extended thaw periods, indicating a transitional regime. In contrast, RG2 shows fewer freeze-thaw cycles and greater thermal buffering, consistent with cold permafrost. The statistical model overestimated thaw dynamics at RG2, highlighting the importance of field-based data for accurate classification. Hydrological signals at RG1-including cold, mineralized meltwater and rapid ground surface temperature stream coupling-are attributed to thawing and deeper flowpaths. Conductivity data (2014-2015) reveal solute pulses consistent with early melt events and debris interaction. Meanwhile, long-term streamflow trends indicate declining discharge. These findings suggest feedback between permafrost loss and water availability. This study underscores the divergent evolution of adjacent rock glaciers under warming by integrating thermal, hydrological, and climatic data. RG1 shows signs of degradation, while RG2 may act as a temporary refuge. Continued monitoring is essential for managing water security in vulnerable mountain regions like the Dry Andes.Graphical AbstractThis graphical abstract visually summarizes a ten-year monitoring effort of mountain permafrost and glacier hydrology in the Navarro Valley, Dry Andes (32 degrees S), with implications for water security under climate change. The left panel situates the study area within the upper Aconcagua Basin, identifying two instrumented sites within the Tres Gemelos rock glacier complex-RG1 (3805 m) and RG2 (4047 m)-and an automatic weather station. These sites were selected for continuous monitoring of ground temperature and streamflow to assess permafrost behavior in a water-stressed mountain catchment. Moving to the center, the image presents an integrated monitoring framework that links temperature-depth profiles, surface-subsurface thermal dynamics, and discharge records. Key indicators such as freeze-thaw cycle counts and thawed-day metrics are used to classify thermal regimes and detect warming trends. The upper-right panel features a conceptual model that connects permafrost degradation to hydrological responses: RG1, characterized as transitional, shows signs of enhanced shallow flow and seasonal meltwater pulses, while RG2 retains cold, thermally buffered conditions that support greater storage stability. These contrasts are further illustrated by temperature trend graphs, which reveal faster warming at RG1 (+ 2.84 degrees C/decade) compared to RG2 (+ 1.92 degrees C/decade), as well as increased thaw metrics. Below, a long-term streamflow graph (1970-2023) documents declining discharge, visually supported by a field photo of a dry riverbed. The bottom panel summarizes the study's key finding: RG1 and RG2 are evolving along divergent thermal and hydrological trajectories, underscoring the need for high-resolution monitoring to guide water resource planning in an era of warming and drought.
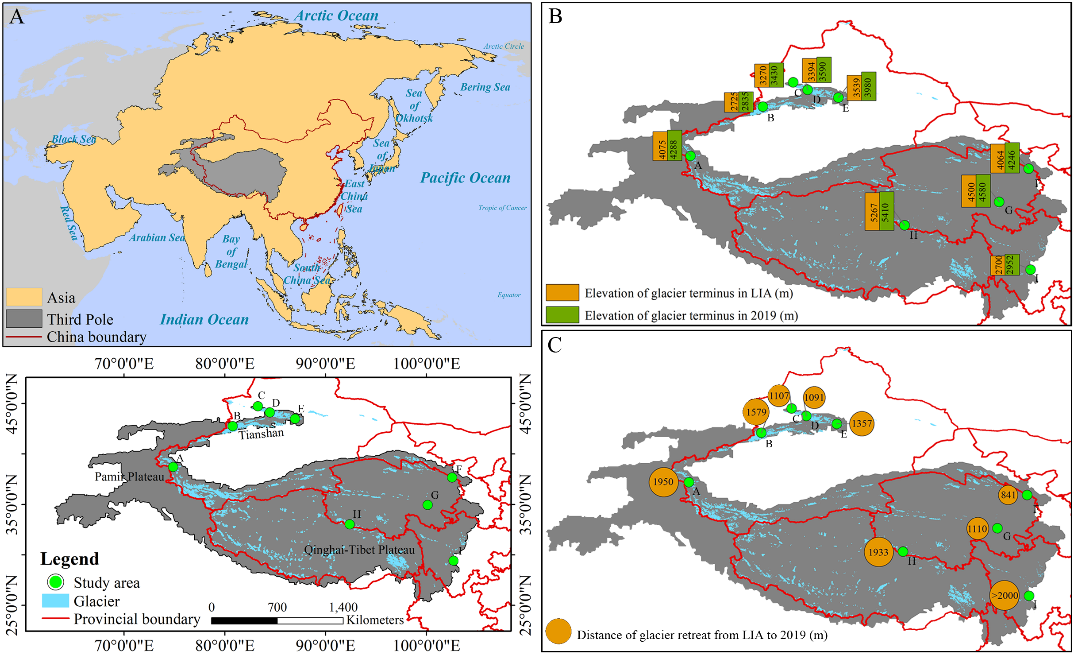
青藏高原及周边高山地区统称为“第三极”地区,是除南北极外最大的冰川集中区。在全球气候变暖背景下,第三极地区正经历显著增温,气温上升加速了冰川消融,进而影响区域生态平衡。第三极冰川前缘作为海拔最高的陆地脆弱生境之一,对气候及冰川变化响应敏感。深入了解冰川前缘植被动态,对科学评估冰缘生态系统响应气候至关重要。然而,受制于观测条件,目前仍缺乏对该地区冰缘植被的大范围系统性观测研究。 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院上官冬辉研究员团队与兰州交通大学、中巴地球科学联合研究中心及南通大学相关研究团队合作,选取第三极地区9条代表性冰川,在其前缘布设样地并获取植被信息。利用植被指数量化了冰川退缩时间序列上植物群落特征的变化,并结合植物区系相似性指数,系统分析了不同样地间及不同冰川前缘间的植物区系相似性。 研究显示,物种多样性和植被盖度沿冰川退缩时间序列呈波动增加趋势,且在海洋性冰川前缘的增加速率尤为显著。所有冰川前缘的植物生活型在演替早期阶段较为相似,但随着演替推进,生活型组成开始分化,在不同类型冰川前缘间差异更为明显。此外,不同冰川前缘间具有植物区系相似性,其中地理位置邻近且属于同一类型冰川的前缘地区植物区系相似性最高。 该研究揭示了局地气候与地理因子在塑造冰川前缘生态系统及植物区系格局中扮演的关键作用,为阐明气候变化对冰川前缘生态系统的影响提供了科学依据,并为区域生物多样性保护工作提供了理论指导。 该成果以Vegetation successional dynamics and floristic similarity across various glacier forelands in the third pole为题发表于国际知名学术期刊Global and Planetary Change上。兰州交通大学魏天锋副教授为本文第一作者,西北研究院上官冬辉研究员为本文通讯作者。研究得到中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(A类)和国家自然科学基金等项目的资助。 论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2025.104916 (A)研究区地理区位图,(B)被研究冰川在小冰期和2019年的冰川末端海拔,(C)被研究冰川在小冰期至2019年间的冰川退缩距离
2025-06-09 中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院Glacier forelands provide ideal natural laboratories for studying primary vegetation succession. However, understanding of vegetation dynamics on glacier forelands in the Third Pole (TP) region remains limited. In this study, we employed field sampling and aerial photography to investigate key vegetation parameters (species composition, species diversity, and fractional vegetation cover (FVC)) along chronosequences on nine representative glacier forelands of the TP, spanning continental, subcontinental, and maritime glacier types, then analyzed vegetation changes along successional gradients and assessed floristic similarity both within and among the glacier forelands. Our results showed that species diversity and FVC generally exhibited increasing trends, with fluctuations from young to old forelands. These parameters increased more rapidly on maritime glacier forelands. Plant life-forms were similar during the early stages across all forelands but began to diverge as succession progressed, particularly between different glacier types. Furthermore, floristic similarity was observed between glacier forelands, with the highest similarity occurring between forelands of the same glacier type in adjacent geographic locations. Our findings highlight the critical roles of local climate and geographic factors in shaping proglacial ecosystems and flora, providing a scientific basis for understanding the effects of climate change on proglacial ecosystems and guiding biodiversity conservation efforts.
Ambient seismic noise and microseismicity analyses are increasingly applied for the monitoring of landslides and natural hazards. These methodologies can offer a valuable monitoring tool also for glacial and periglacial bodies, to understand the internal processes driven by external modifications in air temperature and rainfall/snowfall regimes and to forecast possible melting-related hazards in the light of climate change adaptation. We applied the methods to an almost continuous year of data recorded by a network of four passive seismic stations deployed in the frontal portion of the Gran Sometta rock glacier (Aosta Valley, NW Italian Alps). The spectral analysis of ambient seismic noise revealed frequency peaks related to stratigraphic resonances inside the rock glacier. Although the resonance frequency related to the bedrock interface was constant over time, a second higher resonance frequency was identified as the effect of variations in the active layer thickness driven by external air temperature modifications at the daily and seasonal scales. Ambient seismic noise cross-correlation highlighted coherent shear wave velocity modifications inside the periglacial body. The microseismicity dataset extracted from the continuous ambient noise recordings was analyzed and clustered to further investigate the ongoing internal processes and gain insight into their source mechanism and location. The first cluster of events was found to be likely related to the basal movements of the rock glacier and to falls and slides of the debris material. The second cluster was possibly related to shallow ice and rock fracturing processes. The validation of the seismic results through simple models of the rock glacier physical and mechanical layering, the internal thermal regime and the surface displacements allowed for a comprehensive understanding of the rock glacier's reaction to the external conditions.
Periglacial processes and permafrost-related landforms, such as rock glaciers, are particularly vulnerable to climate change because of their reliance on sustained low temperatures to maintain permafrost integrity. Rising temperatures lead to permafrost thawing, increased active layer thickness, and ground instability, which disrupt the structural and ecological stability of these environments. Rock glaciers, which are ubiquitous in high mountain systems, are especially sensitive to these changes and serve as key geo-indicators of current or past alpine permafrost conditions, reflecting the multifaceted impacts of warming on both ecological and abiotic components. In this review, we synthesize current scientific knowledge on the complex and divergent responses of alpine rock glaciers to climate change, highlighting a wide range of methodologies employed to study the complex interactions between climatic drivers and rock glacier dynamics. We first explore ecological impacts, focusing on how climatic changes influence vegetation patterns, species composition, and overall biodiversity associated with rock glaciers. Subsequently, we examine the dynamic behavior of rock glaciers, including their structural integrity, movement patterns, and hydrological roles within high mountain ecosystems. By integrating findings from various disciplines, this review underscores the importance of multidisciplinary approaches and long-term monitoring to advance our understanding of rock glacier ecosystem dynamics and their role in periglacial processes under climate change. Our synthesis identifies critical knowledge gaps, such as the uncertain drivers of divergent rock glacier responses and the limited integration of ecological and abiotic data in existing studies. We highlight research priorities, including the establishment of regional monitoring networks and the development of predictive models that incorporate vegetation and permafrost interactions. These insights provide actionable guidance for adaptive management strategies to mitigate the ecological and geological impacts of climate change on these unique and sensitive environments.